How Long Does Chlamydia Last?
How chlamydia spreads and how to treat it fast
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the world. The symptoms of chlamydia can be so mild that you don’t even notice them. However, an untreated chlamydia infection can cause serious complications.
The good news is that chlamydia is quickly cleared up in 2-4 weeks. But to treat chlamydia quickly, you need to get tested for prompt treatment. This article will detail some basic facts about chlamydia, including how long it lasts and how to treat it fast.
Symptoms and Causes of a Chlamydia Infection
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection of the Chlamydia trachomatis bacterium. It is a sexually transmitted infection—also known as a sexually transmitted disease (STD)---spread through sexual contact with an infected person.
This includes:
- Vaginal sex
- Oral sex
- Anal sex
Pregnant women can also spread chlamydia to their newborns during delivery.
The early signs of chlamydia are often mild. Sometimes, early symptoms are so mild that they go unnoticed. These symptoms usually appear a week or more (7-21 days) after unprotected sex. Many people with chlamydia, especially women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB), may never develop symptoms at all.
Symptoms of chlamydia include:
- Vaginal discharge
- Discharge from the urethra (in people with a penis)
- Burning sensation during urination
- Pain or swelling in the testicles (in people with a penis)
- Pain during sexual intercourse (in people with a vagina)
- Pelvic pain (in people with a vagina)
Chlamydial infections can also affect the rectum, eyes, and throat. Rectal infections from anal sex may cause discharge or pain.
A chlamydia eye infection—conjunctivitis— leads to redness and swelling in the eyelid.
Chlamydia infections of the throat cause symptoms like:
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Mouth sores
- Mouth pain
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the infection.
Complications from Untreated Chlamydia
Untreated chlamydia can result in complications like:
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) (in women): An infection that can cause permanent damage to the uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes. It may result in infertility.
Epididymitis (in men): An infection of the tube beside each testicle (known as the epididymis). This can cause pain, swelling, and a fever. Reactive arthritis: Reactive arthritis causes inflammation in the urethra, joints, and eyes.
Ectopic pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg grows outside of the uterus. This can cause vaginal bleeding and pain in the pelvis. In some cases, an ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening unless it is surgically removed. Chlamydia can cause this by causing scarring in the fallopian tubes which prevents the egg from reaching the uterus normally.
Chlamydia spread to newborns: Newborn babies can contract chlamydia from the vaginal canal during birth. This can lead to pneumonia, lung infections, or eye infections in the baby.
Infertility: Untreated chlamydia can scar the fallopian tubes, leading to infertility in women.
Targeted chlamydia treatment is crucial in preventing these complications.
How Long Chlamydia Lasts
Now for the good news: chlamydia is curable.
It can be hard to tell if you have a chlamydia infection. In some cases, chlamydia causes no symptoms. But if chlamydia is left untreated, it can live in the body for months or years. The infection will not go away on its own. However, prompt antibiotic treatment may help the infection clear up within 2-4 weeks. You may notice your symptoms getting better after a few days of taking antibiotics.
The treatability of chlamydia, as well as the risk of spreading the disease during sexual activity, underlines the importance of getting tested for chlamydia and other STIs. The sooner you get tested, the sooner you get treated, and the sooner your symptoms will go away. This also prevents you from transmitting the disease to other sexual partners.
When to Get Tested for Chlamydia
STI testing is crucial for sexual health. Specific guidelines vary depending on anatomy and sexual history.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers general recommendations for STI testing. Below is an overview of these guidelines.
Women:
- Sexually active women under 25 should be tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea at least once a year.
- Women over 25 who have unprotected sex, multiple sex partners, or sex with a partner who has an STI should be tested at least once a year.
- Rectal chlamydia testing may be considered if the patient has had anal sex.
Pregnant women:
- All pregnant women should be tested for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and chlamydia.
Men who only have sex with women:
- Men in high-prevalence settings like sexual health clinics or correctional facilities should be tested for chlamydia every year.
Men who have sex with men:
- Men who have sex with men should be tested for oral and rectal chlamydia every year, whether or not they use condoms.
- Men who have sex with multiple partners, men who have an HIV infection, or men who are on pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV should be tested every 3-6 months.
Transgender and gender-diverse people:
- Testing recommendations are based on anatomy.
- Transgender men and gender-diverse people with a cervix should be tested for chlamydia every year.
- Testing for rectal and oral chlamydia should be considered based on sexual behaviors.
People with HIV:
- People with HIV who are sexually active should be tested for chlamydia at least once a year.
Regular STI testing protects your health. It also prevents you from spreading infections to other sexual partners. For more information, check out the CDC’s STI Screening Recommendations.
How chlamydia testing works
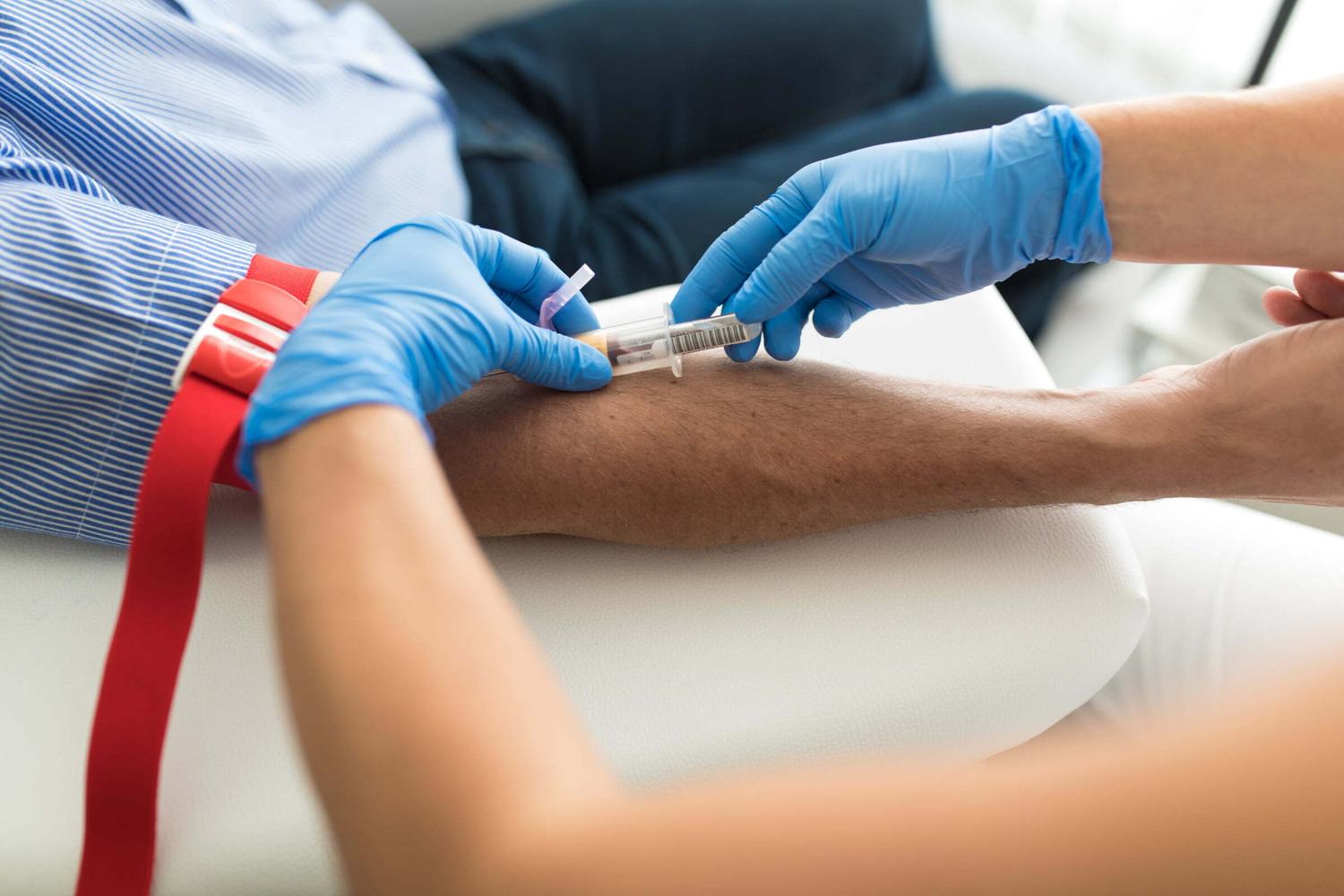
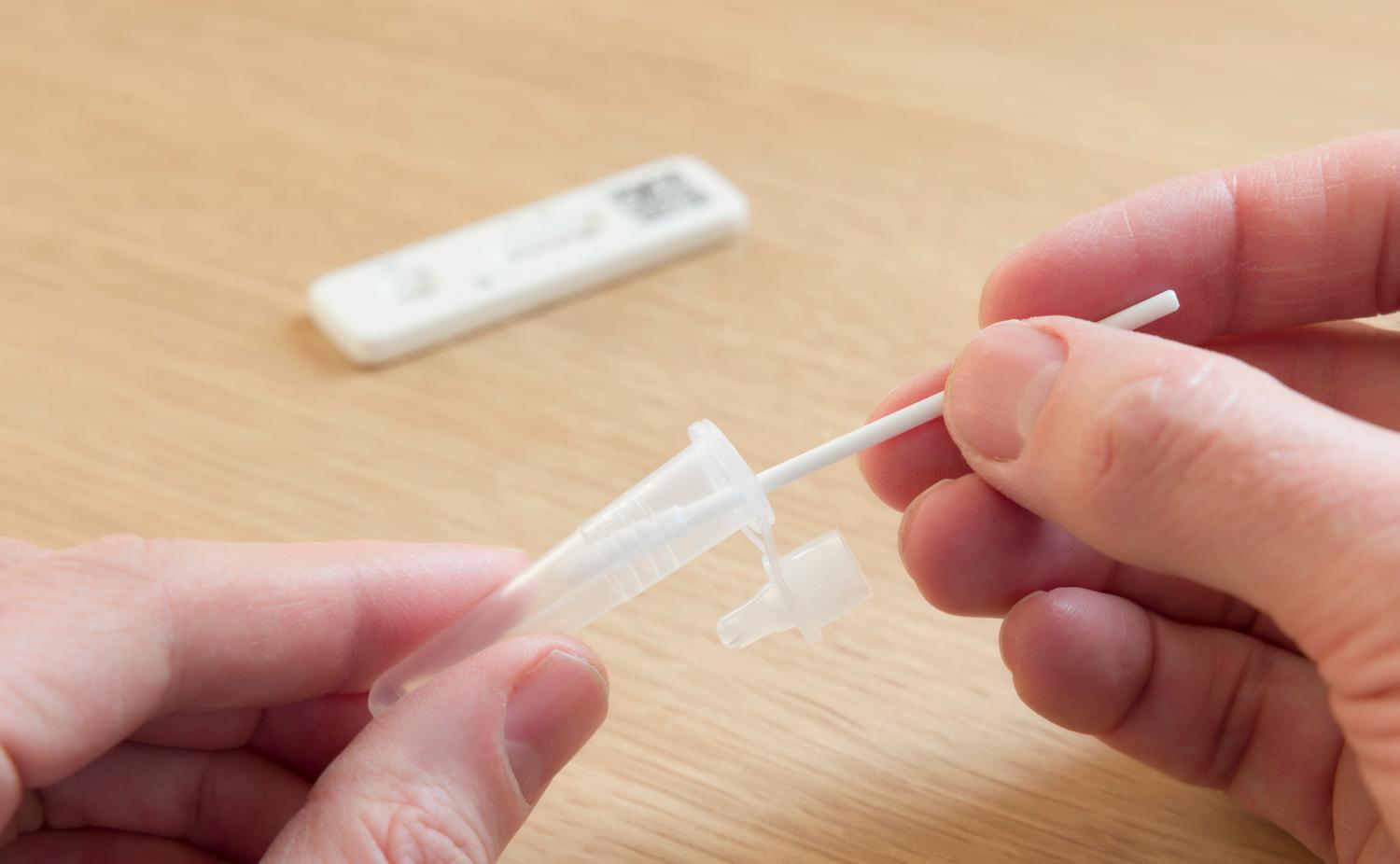
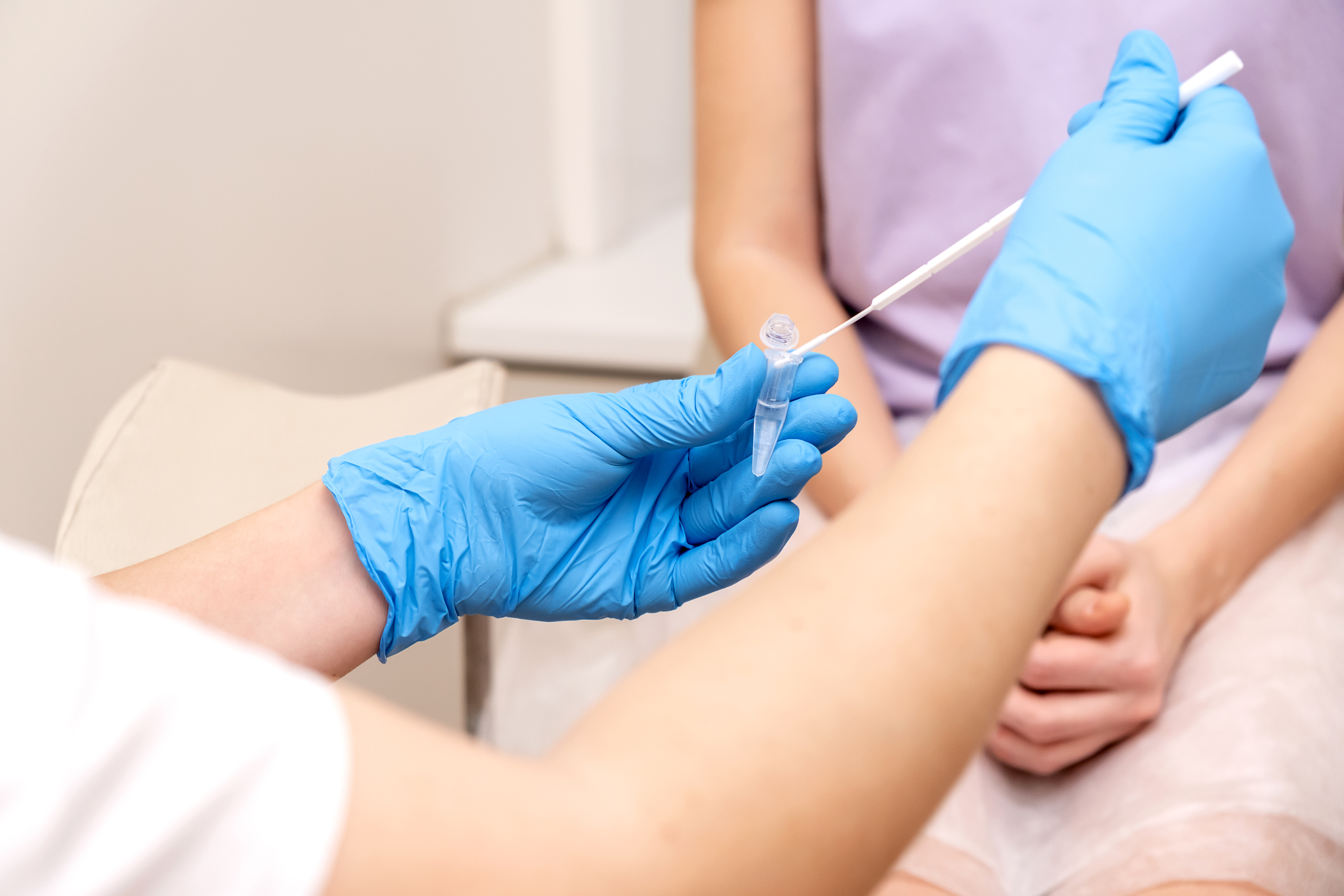
You can get a chlamydia test at a sexual health clinic or a primary care office. Urine tests may be performed at your home. To test for chlamydia, healthcare providers will perform one of these tests:
Urine sample: Urine tests show chlamydia bacteria in the urine. You will usually get your test results within 2-5 days.
Blood test: Blood tests check for the presence of chlamydia antibodies (cells that are released to fight the infection). If these antibodies are in your blood, you likely have an infection. If the clinic can process blood on-site, you may be able to get your results within a few hours. If they need to send your blood sample to a separate lab, getting your test results may take several days to a week.
Swab test: Swab tests can be performed on the urethra, cervix, anus, or throat. The swab collects fluid from these areas to check for chlamydia bacteria. You will usually get your test results within 2-3 days.
How to Cure Chlamydia Fast
If treated quickly, chlamydia will clear up within two weeks. Because chlamydia is a bacterial infection, it must be treated with a course of antibiotics. Swift treatment will clear up the infection while preventing reinfection.
The most common antibiotics used for treating chlamydia are:
- Azithromycin
- Doxycycline
These drugs are given as a pill to be taken orally (by mouth).
You may be given a single dose of antibiotic medication or a course of treatment lasting a week. Your healthcare provider will give you specific directions on how to take your medication and how long you should use it.
Do not stop taking your medication even if you start feeling better. Not finishing the entire course of treatment can cause the infection to return. Take your antibiotics as instructed, and tell your provider if you begin to notice any side effects during treatment.
If you test positive for chlamydia, you should get tested for additional STDs such as gonorrhea, HIV, and syphilis.
How Sesame Can Help
Be proactive about your sexual health. If you have questions about chlamydia or any other sexually transmitted infection, book an online doctor’s appointment to speak to a licensed healthcare provider today. If you want to get tested, Sesame offers low-cost, at-home chlamydia and gonorrhea testing kits powered by Ash for both males and females. These kits are delivered in discreet packaging within 3 days of ordering. Return shipping is included in the price of the test. Your test results will be delivered to you via a confidential patient portal.