UTIs in Men: What You Need to Know
What you need to know about urinary tract infections (UTIs) in men
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are bacterial infections of the urinary tract. They are far more common in women than in men, but that does not mean that men are immune. About 12-20% of men will get some type of UTI.
This article will explore the causes and symptoms of urinary tract infections in men, as well as treatment options and ways to prevent UTIs from occurring.
UTI Symptoms in Men
Because UTIs don’t happen in men that often, it can be hard to tell if you have one. In addition, the symptoms of a UTI may vary. Some men experience no symptoms at all, while others experience severe discomfort.
Common UTI symptoms include:
- A strong and persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation while urinating (dysuria)
- Frequent urination with little volume
- Cloudy or hazy urine (scarlet, pink, or cola-colored urine is a sign that there is blood in the urine)
- Strong smelling urine
- Pressure or cramping in the genital area or lower abdomen
- Back pain (common with kidney infection)
Causes of UTIs in Men
Urinary tract infections are commonly caused by bacterial infections—usually from the E. coli bacterium. The bacteria enter the body through the urethra (the small tube in the penis through which urine is carried), making its way up through the urinary system, which consists of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra.
Your body has natural defenses against E. coli, but sometimes these fail, and the bacteria can spread throughout the internal organs, resulting in an infection. E. coli can be carried from the rectum into the urethra, causing infection. However, this infection is more common in women than men (due to shorter urethras).
Risk factors for UTIs in men include:
- An enlarged prostate gland (also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH)
- Blockage of the urinary system
- Age (UTIs are more common in older men)
- Dehydration
- Sexually transmitted diseases (especially chlamydia and gonorrhea)
- Anal sex
- Kidney stones
- Diabetes
- Abnormal narrowing of the urethra (known as “stricture”)
- Urinary catheter use
- A compromised immune system
- Not being circumcised
- Bowel incontinence (not being able to hold your bowel movements until you get to a toilet)
Types of UTIs in Men
There are two types of urinary tract infections: upper and lower tract infections.
Lower tract infections
A lower tract infection is either a bladder infection (cystitis) or a urethra infection (urethritis).
Lower urinary tract infections in men are most often caused by sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. These sexually transmitted infections are more common among younger men. Men who have anal intercourse are also at higher risk of UTIs.
Upper tract infections
Upper-tract infections include ureter infections and kidney infections (pyelonephritis).
Upper urinary tract infections may be caused by a blockage in the urinary system. A blockage causes urine to build up and stagnate, encouraging bacterial growth. Kidney stones, catheter use, or an enlarged prostate gland may cause blockages in the urinary system.
UTI Complications in Men
When adequately treated, UTIs disappear within a day of starting treatment. If left untreated, however, they can cause serious complications.
Complications from a urinary tract infection include:
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Kidney infections
- Kidney diseases
- Sepsis—a life-threatening medical emergency
Because these complications can be potentially life-threatening, you must seek medical attention from a healthcare provider when you notice symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
Contact a primary care provider or a urology doctor (a urologist) when you notice the early signs of a UTI. These signs may include strong-smelling urine, pain during urination, and back or abdominal pain.
Healthcare providers will test you for a UTI and prescribe treatment if necessary. Early treatment will help symptoms go away quickly while preventing the complications listed above.
What to expect from a UTI appointment
Providers use a urine test to detect a UTI. This test is known as urinalysis, and it involves taking a culture from a urine sample.
During your appointment, you will likely be asked about your symptoms, your health history, and your sexual history. After this overview, your healthcare provider will ask for a urine sample to test. The sample will be examined under a microscope to check for abnormalities like excessive white blood cells or harmful bacteria.
If your provider suspects an internal problem is causing your UTI, you may be asked to undergo additional testing. Additional tests are usually performed at a urology clinic. Your urologist may request an X-ray or CT scan to see what is causing the UTI. The urologist may perform a cystoscopy if the infection is in the bladder. Cystoscopy is a procedure in which a tiny camera is inserted into the urethra and passed into the bladder to check for potential problems.
After testing, your care team will discuss treatment options with you. Treatment will depend on what is causing your UTI.
UTI Treatment
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. This is the best way to treat a UTI fast. Antibiotics kill the invasive bacteria while preventing their spread to other body parts.
Standard antibiotic treatment options for UTIs include:
Your symptoms will start feeling better within about a day, but they may take a week to go away entirely. Even if you start feeling better, take the whole course of antibiotics. If you stop taking your medication before the infection has been completely treated, it may return. Follow your doctor’s orders regarding your prescription and ask any questions you may have before starting treatment.
Antibiotics have been shown to cause some mild side effects. These include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Skin rash
If these symptoms become severe, or if your UTI doesn’t start feeling better after a few days of antibiotic treatment, talk to a healthcare provider right away.
There are no over-the-counter or home remedies that can adequately treat a UTI. However, there are OTC medications you can use to ease pain and discomfort from a UTI. There is little evidence that non-prescription treatment options like cranberry juice or probiotic supplements can treat a urinary tract infection.
How to Prevent UTIs
Not all urinary tract infections are avoidable. However, you can cut down on your risk of developing one by practicing these easy preventative measures:
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Go to the bathroom as soon as you feel the urge to do so, and be sure to empty your bladder completely
- Use a condom while having sex
- Urinate shortly after having sex
- Maintain good genital hygiene
- Wash under the foreskin when you take a bath or shower (if you are uncircumcised)
While some UTIs are unavoidable, these tips can help minimize your risk of developing one.
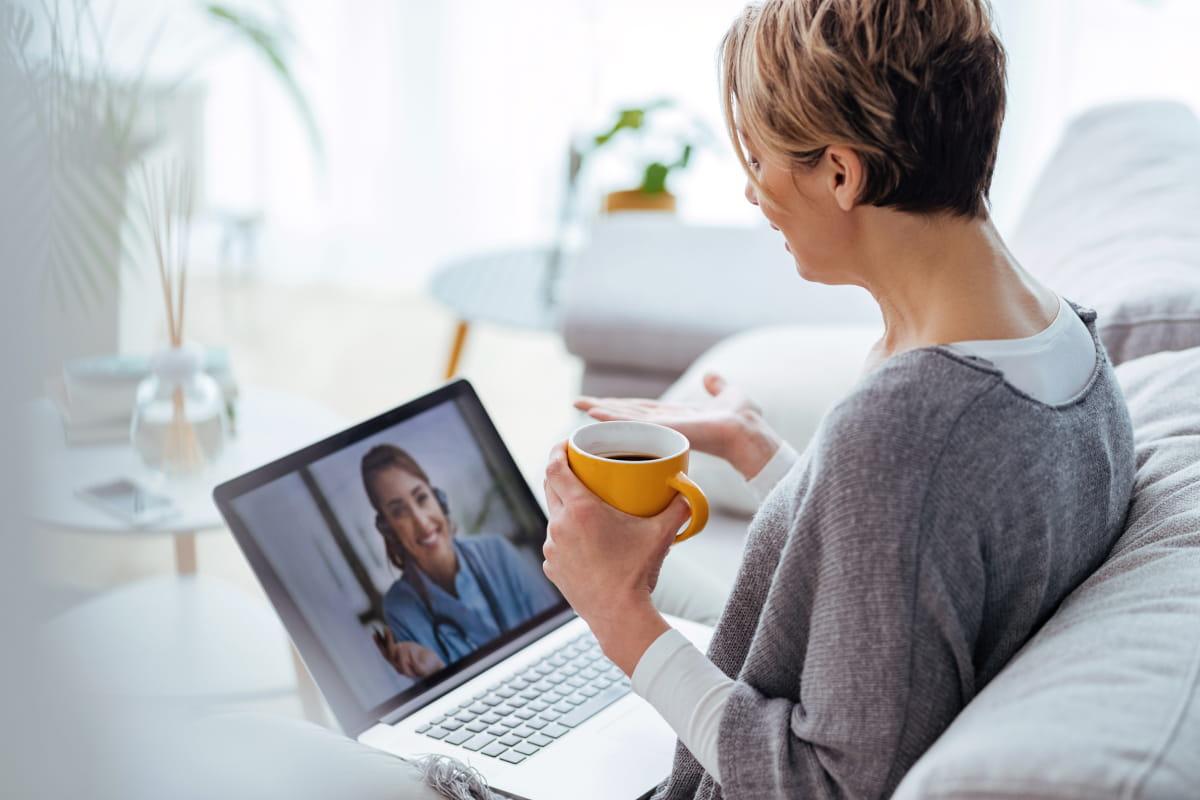
How Sesame Can Help
UTIs are painful and dangerous. If you notice a UTI's early signs and symptoms, book an online doctor appointment on Sesame to discuss your concerns with a licensed healthcare provider. Video visits on Sesame offer the opportunity to get same-day care without going to an office or clinic. If appropriate, providers can prescribe antibiotics to be picked up at your local pharmacy. Don’t wait to treat a UTI. Book a visit on Sesame and start feeling better right away.