Bug Bite Relief: How to Treat Itching, Stinging & More
Key Takeaways
- Most bug bites and stings are mild and will go away on their own within a few days
- Over-the-counter (OTC) medicine and home remedies can treat itchy skin and irritation from these wounds
- You should seek medical attention for severe symptoms like significant swelling, trouble breathing, or hives
Most bug bites and stings aren’t dangerous and reside within a few days. However, they can still be incredibly uncomfortable. Even a small bite can lead to persistent itching, swelling, or irritation that gets in the way of your day (or your sleep).
These reactions happen because your body sees the bug’s saliva or venom as a threat. In response, it releases histamines, chemicals that trigger redness, swelling, and that all-too-familiar itch.
Some common types of bug bites include:
- Mosquito bites
- Fire ant bites
- Spider bites
- Flea bites
- Bed bug bites
- Fly bites
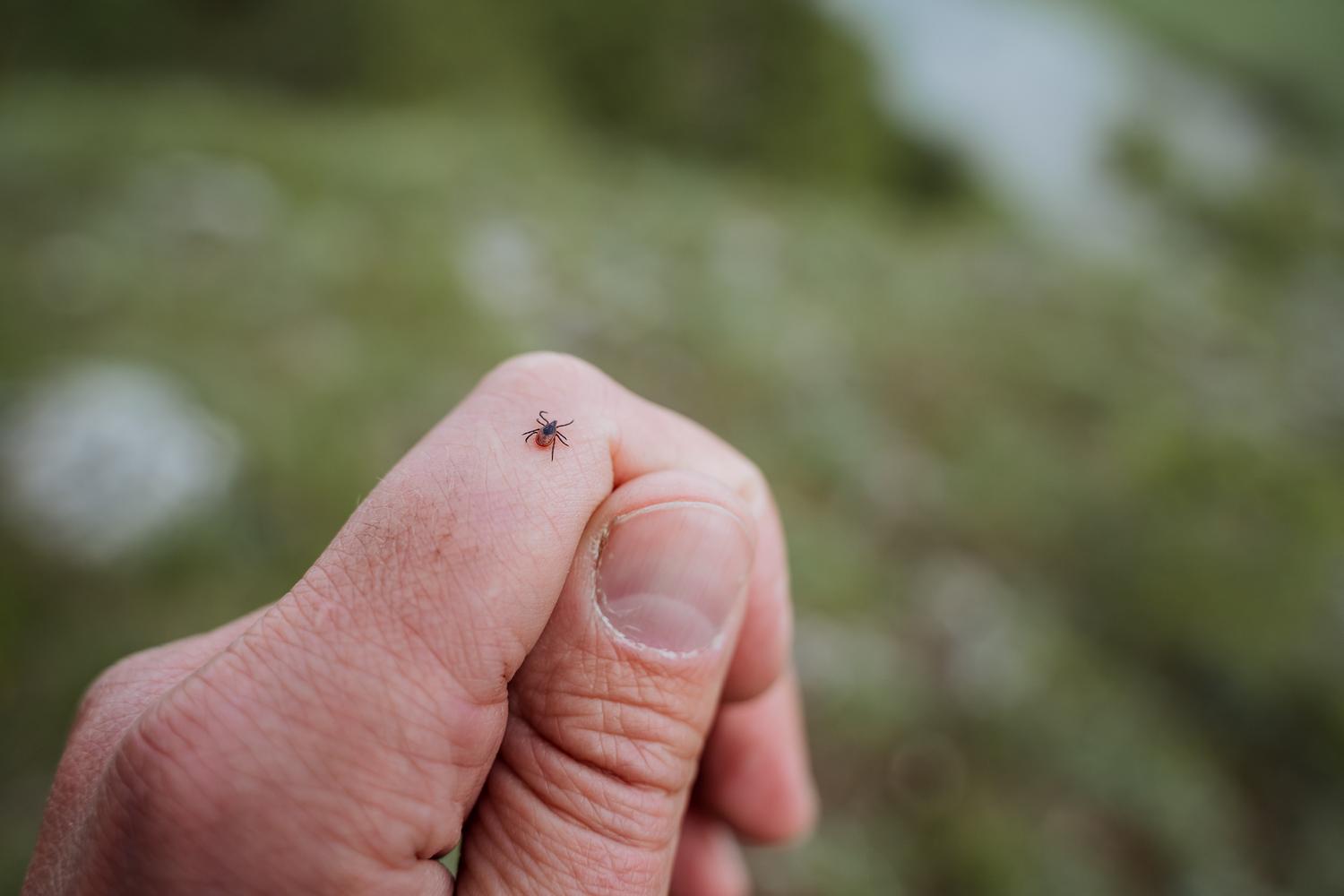
- Tick bites
- Chigger bites
Luckily, there are several over-the-counter and at-home treatment options for bug bites and stings. Let’s explore the most effective ways to treat itching and stinging at home.
How to treat bug bites
From OTC medications to easy home remedies, there are plenty of ways to find relief from a bug bite. Some treatments help by reducing inflammation and allergic responses, while others work to cool, numb, or moisturize irritated skin.
Let’s explore the most effective options for easing bug bite symptoms at home.
OTC medications for bug bites
Over-the-counter medicine for bug bites limits the immune system’s allergic reaction and soothes bug bite symptoms. Common OTC medications include:
OTC anti-itch treatments
Topical anti-itch treatment is widely available as medicated creams, ointments, or lotions applied to affected skin.
Common anti-itch treatments for bug bites include:
- Calamine lotion: Calamine lotion contains the mineral calamine, which has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. Apply a thin layer of calamine lotion to itchy skin several times a day until your symptoms start to go away.
- Hydrocortisone creams: Medicated anti-itch creams like Cera-Ve and Cortizone work by reducing your body’s immune response to a bug bite. This eases inflammation, redness, and itchiness caused by bug bites.
- Benadryl cream: Benadryl topical cream is a medicated cream that relieves pain and itching from bug bites.
- #### OTC antihistamines Antihistamine drugs work to counter your body’s allergic response, which can reduce inflammation and itchiness.
Common OTC antihistamines for bug bites include:
Oral antihistamine pills start working within 30 minutes. Take oral antihistamines as directed on the medication’s packaging. Do not exceed the dosage recommended on the drug label.
If you are giving an antihistamine to a child, look for a formulation specifically for children (like Children’s Zyrtec). Follow the instructions on the drug’s packaging.
OTC antihistamines are generally mild and well-tolerated. If you notice any side effects like swelling or trouble breathing, seek medical attention immediately.
OTC pain relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers can treat pain and inflammation caused by bug bites. After cleaning the bite and applying an anti-itch medication, adults can take a non-prescription pain reliever.
Common OTC pain reliever options for bug bites include:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Ibuprofen (Advil)
Follow the dosing instructions on the medication’s packaging. If you give an OTC pain reliever to a child, look for a formulation that works for kids or check the packaging to ensure it is safe for young people.
Seek medical attention if you begin to notice side effects of OTC pain reliever usage, like stomach pain or nausea.
At-home remedies for bug bites
In addition to OTC medicine, you can use several home remedies to relieve your symptoms. These include:
- Baking soda paste: Baking soda has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties, which can reduce itching and redness caused by bug bites. Mix 1 tablespoon of baking soda with enough drops of water to make a thick paste. Apply this mixture to clean the skin and let it sit for 10 minutes before washing it off.
- Ice packs: Ice can reduce inflammation while temporarily numbing the skin, easing itchiness and discomfort. Wrap an ice pack or crushed ice in a clean, damp towel and apply it to the affected area. Hold the towel on your skin for 10-20 minutes. Do not apply ice directly to the skin.
- Witch hazel: A limited study showed that witch hazel may help reduce skin inflammation and irritation. You can buy witch hazel in the facial care aisle of supermarkets and retailers. Apply a few drops to a cotton ball and dab this on the irritated skin.
- Heat: A study of 1,750 participants found that targeted heat treatment reduced itching from bug bites within 1 minute. Use a heat device like heat it ™ (which you control with your smartphone) to relieve the symptoms of a bug bite.
- Peppermint oil: Essential oils, specifically peppermint oil, may be able to reduce itching symptoms. However, no specific scientific evidence exists that peppermint oil helps treat mosquito bites.
- Colloidal oatmeal: Colloidal oatmeal is commonly used to treat itchy, inflamed skin and can ease symptoms from a bug bite. You can buy oatmeal bath powder in most pharmacies. Empty the packet into warm (not hot) water and soak for 15-30 minutes. This works particularly well when you have multiple bites.
Most mosquito bites and bites from other insects will disappear within a few days. However, bed bugs, fleas, ticks and lice may require more advanced treatment. If you think you have been bitten by one of these insects, talk to a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment. You may need to contact a pest control agency to de-infest your living space.
You should book a tick bite appointment right away if you think a tick has bitten you. Ticks spread Lyme disease and other illnesses that can cause serious complications if left untreated, so seeking prompt medical care is crucial to avoid severe health problems.
How to treat stings
Insect stings can cause red, puffy, and painful welts on the skin.
Common types of stings include:
- Bee stings
- Yellowjacket stings
- Hornet stings
Here’s how to treat a sting:
- Calmly move away from the area where you were stung to prevent further stings
- Remove any stingers in your skin by scraping at them with your fingernail or a piece of gauze
- Do not squeeze the stinger or try to remove it with tweezers, as this can force more venom from the stinger (making the wound worse)
- Wash the sting spot with gentle soap and warm water
- Apply an ice pack or crushed ice wrapped in a cool, clean towel to the affected area
- Keep the ice pack on the sting for 10-20 minutes
- For adults, consider taking an OTC pain reliever like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to help with pain
Watch for the signs of an allergic reaction to the sting. While not common, allergic reactions to bee, wasp, or hornet stings can cause life-threatening anaphylaxis.
Keep an eye out for symptoms such as:
- Hives
- Skin rash
- Worsening swelling
- Facial swelling
- Difficulty breathing
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Wheezing
Bug bite and sting prevention tips
With a few preventative strategies, you can reduce your risk of bug bites and stings. These include:
- Apply an insect repellant with DEET
- If going outside, spray all clothing, shoes, tents, and outdoor gear with an insect repellant that contains 0.5% permethrin
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants to reduce your skin exposure
- Avoid wooded areas or areas with long grass
- When hiking, walk in the center of trails to avoid contact with surrounding plant life
- If hiking or camping, bring a first aid kit with you (just in case)
When to see a doctor
If you have been bitten or stung by an insect, watch for severe symptoms like significant swelling, hives, or trouble breathing. These are often the early signs of a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction and should receive medical attention immediately.
If you start noticing symptoms like a skin rash, fever, blisters, or body aches after a bite or sting, talk to a primary care provider or dermatologist as soon as possible. These are early signs of an infection that requires advanced treatment.
How Sesame can help
If you have a mild bite or sting or have questions about treating a wound from a bug, book an online urgent care appointment on Sesame to speak to a licensed healthcare provider right away via video. Providers on Sesame can offer medical advice and prescribe medication if appropriate.