STI Awareness Month: What You Need To Know
STI education leads to a happier, healthier you.
Did you know that 1 in 5 Americans have a sexually transmitted infection (STI)? That’s right: according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), almost 70 million people in the United States are dealing with an STI.
Even though STIs are common, many people find them difficult to discuss because of stigmas or lack of awareness. Because of this, some are reluctant to seek information, testing, and treatment - and STI rates are on the rise as a result. For example, syphilis rates increased by 80% from 2018 to 2022.
Luckily, April is STI Awareness Month, which serves as a great opportunity to promote education, open dialogue, and preventive measures.
To raise awareness about STIs, we’ve compiled some important facts about STIs below. Read on for helpful information on how to speak with your partner(s) about safe sex, how to protect yourself and others, and testing and treatment options.
STIs: Understanding the basics
STIs are infections transmitted through sexual contact and are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. There is no difference between STIs and STDs (sexually transmitted diseases).
STIs can impact any age group. Data from the CDC has found that almost half (46%) of new STIs in the United States occur with young people between the ages of 15 and 24. However, rates have also skyrocketed for those aged 55 and up in the last 10 years. These statistics highlight why it’s important to have conversations about sexual health no matter what age you are.
Common STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, and human papilloma virus (HPV). These infections can have a range of symptoms, from mild irritations to severe health complications.
Health risks of STIs
STIs can be seriously harmful to your health. Some STIs are also asymptomatic, meaning they can go unnoticed and untreated for long periods. This can increase the risk of transmission and serious health problems. Health problems that can arise as a result of STIs include:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Often caused by untreated gonorrhea and chlamydia, PID can lead to severe pelvic pain and damage to the female reproductive organs. This damage can make it difficult or impossible to get pregnant. PID can also increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy, a life-threatening condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus.
- Infertility: Both men and women can become infertile as a result of reproductive health damage caused by STIs like chlamydia and gonorrhea. Increased risk of HIV/AIDs: Certain STIs, especially those that cause ulcers, can increase the risk of acquiring or transmitting HIV.
- Cervical cancer: Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a major cause of cervical cancer, as well as some other types of cancer.
- Orchitis: This is an inflammation of one or both testicles, which can be caused by STIs like gonorrhea and chlamydia.
- Neurological problems and cardiovascular disease: Untreated syphilis can progress to neurosyphilis. This is a condition that affects the brain and nervous system, and can also cause damage to the heart and blood vessels.
- Congenital infections: Pregnant women with untreated STIs are at risk of passing the infection to their babies during childbirth. This can lead to stillbirth, neonatal death, low birth weight, and congenital infections such as congenital syphilis.
5 ways to talk about STIs and STDs with your partner
Initiating conversations about STIs can feel challenging and even scary. However, it’s essential for maintaining a healthy sexual relationship. It means that you and your partner(s) have mutual respect for eachother. Plus, talking openly with your partner(s) about sex and sexual health is a great way to encourage fun, honesty, and satisfaction in your relationship!
Some topics to cover include when you were last tested for STIs, how often you get tested for STDs, and your results. Here are some tips for discussing STIs with your partner(s):
- Choose a comfortable environment: Opt for a private, comfortable setting where both parties can focus on the conversation.
- Be honest and direct: Clearly express your concerns and experiences while encouraging your partner(s) to do the same. Offer support: If you or your partner(s) need testing or are dealing with an STD, lend a hand with finding a testing center or seeking treatment options. This can make all the difference!
- Remain calm and supportive: Approach the discussion with empathy and understanding. Avoid judgment, blaming and shaming. Try to put yourself in the shoes of your partner(s) and practice empathy.
- Listen to your partner(s): Give your partner(s) time to process information and respond. Be prepared for a range of emotions and questions. Listening is just as important as sharing your own thoughts and concerns!
5 ways to protect yourself and your partner
STI prevention is a crucial aspect of sexual health. By adopting safe sex practices like regular screenings and using barrier methods such as dental dams or condoms, you can significantly reduce the risk of contracting or transmitting STIs. The methods below can all play a effective role in protecting yourself and your partner:
- Use barrier methods: Consistently and correctly using condoms and dental dams can help prevent the spread of STIs. If you’re not sure how to go about using barrier methods, a healthcare provider can offer guidance.
- Get vaccinated: Vaccinations are available for some STIs, such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and Hepatitis B. Many health insurance companies cover these vaccines, and there are also patient assistance programs and cost-saving coupons for those who are under-insured or uninsured.
- Communicate openly: Discuss your STI status and prevention methods with potential partners before engaging in sexual activity.
- Get regular check-ups: Regular sexual health screenings can help detect and treat STIs early, minimizing their impact on your health and fertility.
- Talk with a provider about PrEP: PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) is a type of HIV prevention drug. It protects uninfected individuals from becoming infected. If you’re HIV-negative and have a sexual partner who’s living with HIV, or if you’re at high risk for HIV, speak with your healthcare provider to see if PrEP is right for you.
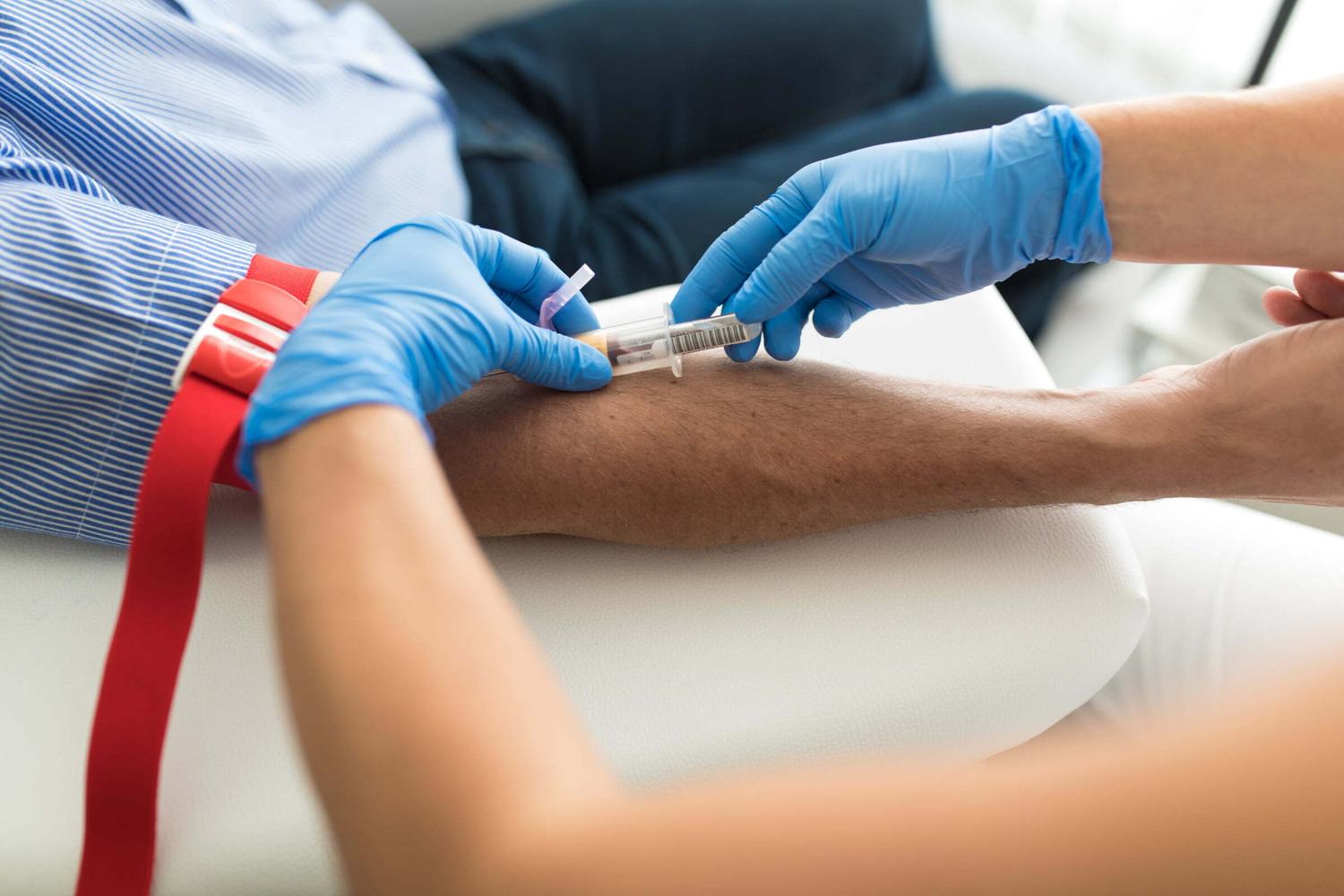
Testing for STIs
Regular STI testing is vital for anyone who is sexually active. Early detection can prevent long-term complications and reduce the risk of transmission to others:
- Know the recommended tests: Familiarize yourself with the standard tests for STIs, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV, and HPV.
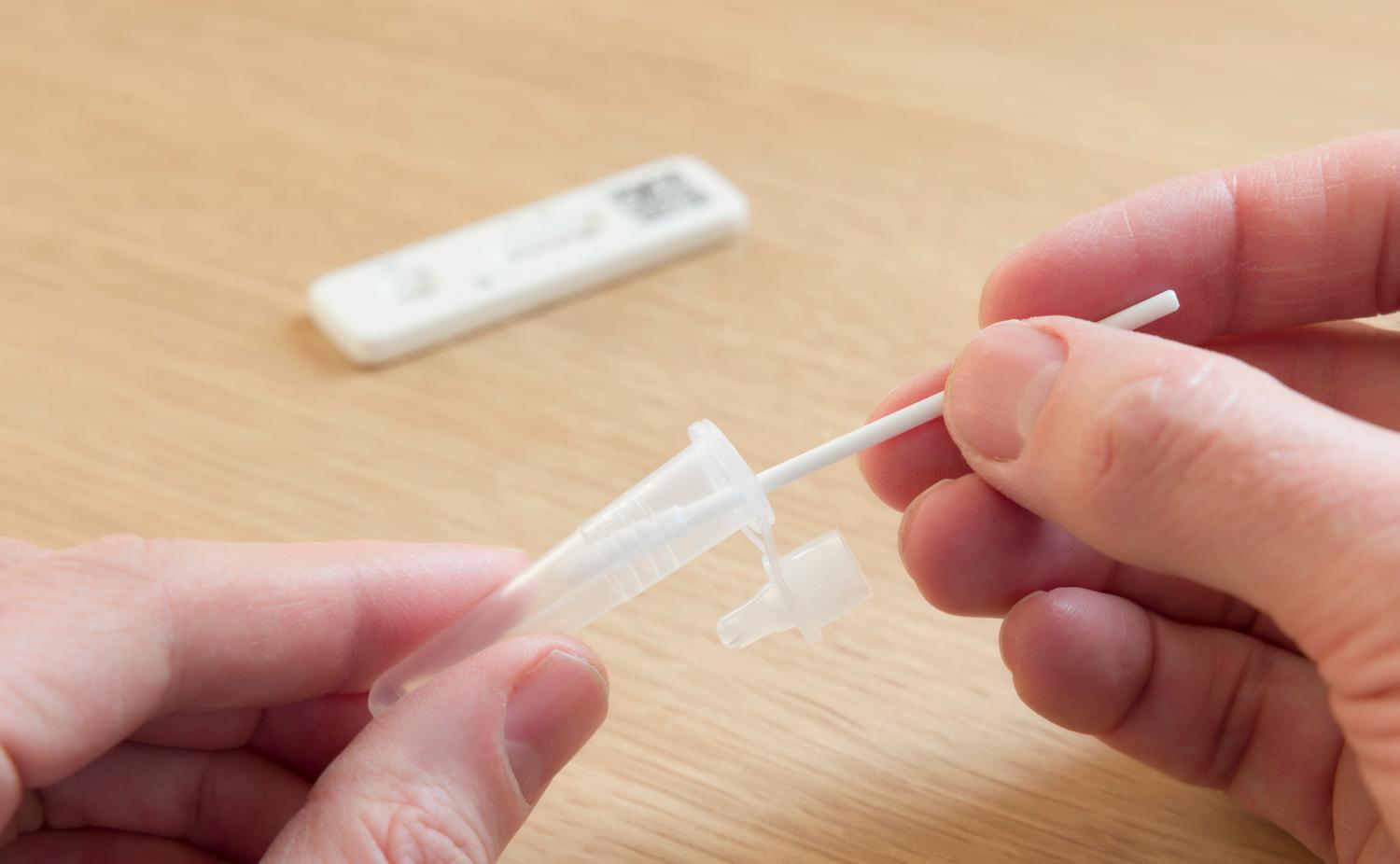
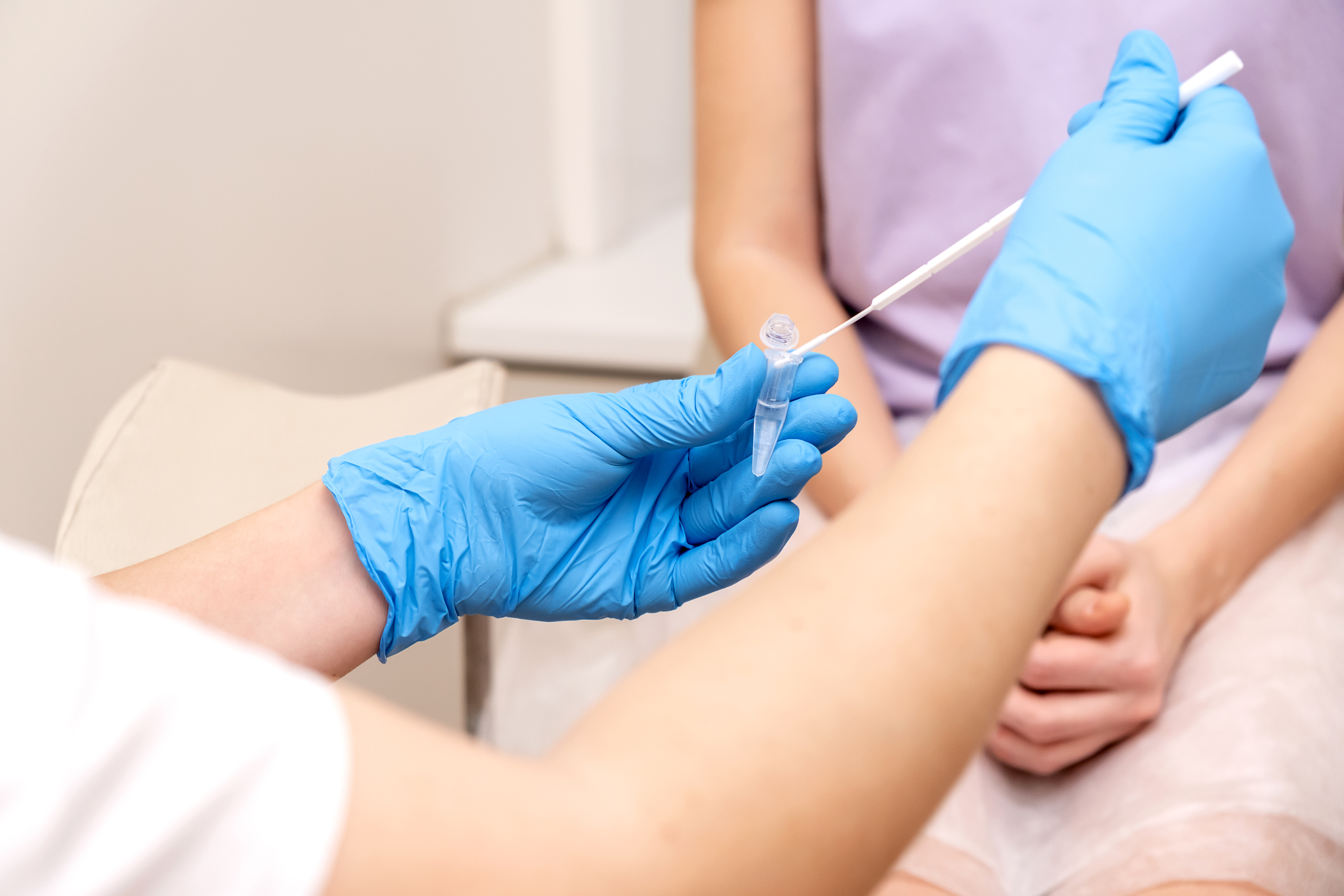
- Understand the testing process: STI tests can include blood tests, urine tests, swabs, or physical examinations, depending on the infection being tested for.
- Identify your testing schedule: The frequency of STD testing depends on your age, sexual activity, and risk factors. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
- Find a testing facility: Many clinics, hospitals, and community health centers offer STI testing. Some organizations even provide free or low-cost testing services.
- Order at-home tests: You can actually test for a number of STIs from the comfort of your own home. You can purchase kits online or from your local pharmacy. You can also order kits through Sesame At-Home Labs Powered by Ash. These at-home tests can detect STIs including chlamydia, gonorrhea, HIV and more.
STI Treatment Options:
Timely and appropriate treatment is crucial to prevent complications, protect sexual partners, and curb the spread of STIs. Luckily, there are a wide range of treatment options available!
Treatment will depend on the type of STI, the severity of the infection, and the individual's medical history. A healthcare professional can help determine the right diagnosis and treatment. Treatment options for common STIs include:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis, antibiotics are often the first line of treatment. The choice of antibiotic, dosage, and duration depends on the specific infection and individual factors. Commonly prescribed antibiotics for STIs include doxycycline, azithromycin, amoxicillin, tetracycline, and penicillin. Providers will typically prescribe medication for both you and your partner(s), since all parties will need to be treated in order to prevent the infection from recurring.
- Antiviral medications: For viral infections such as herpes, HIV/AIDs and human papillomavirus (HPV), antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks.Common antiviral medications for STIs like herpes and HPV include acyclovir (generic Zovirax), famciclovir (generic for Famvir), and valacyclovir (generic Valtrex).
- Topical treatments: Creams and ointments can be used to alleviate itching, irritation, and inflammation caused by certain STIs like genital warts and herpes outbreaks. Common topical treatments include imiquimod and podofilox.
- Partner treatment: It is essential for sexual partners to be treated simultaneously to avoid reinfection and reduce the spread of STIs.
STI Awareness Month serves as a powerful reminder to prioritize sexual health through open dialogue, prevention, and testing. By embracing these practices and encouraging others to do the same, you can take charge of your sexual health and contribute to a healthier society.
How Sesame can help
Let’s talk about sex! Whether you have a sexual health query, need an STI test or treatment for you and your partner, or are looking for assistance with managing an existing STI, Sesame can help.
Our providers offer discreet and affordable same-day online visits for sexual health to ensure that you can get the answers and care you need with ease and privacy. Your well-being is our top priority, and we're committed to providing you with the care and treatment you need to stay healthy and informed.