Eczema vs. Psoriasis: Key Differences and Similarities
Key Takeaways:
- Eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions with different underlying causes; eczema often results from a weakened skin barrier and leads to inflamed, itchy patches, while psoriasis is an autoimmune condition causing rapid skin cell growth and thick, scaly patches.
- Both conditions share common triggers like stress, weather changes and skin injuries, but they differ in symptoms: eczema causes intense itching and dry, sensitive skin, while psoriasis typically results in burning sensations and thick, red, flaky patches.
- Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, light therapy, and specific medications, but what works best varies by individual and condition. Eczema may also be treated with antihistamines, while psoriasis may benefit from biologics and salicylic acid creams.
Understanding eczema and psoriasis: Key differences, similarities and treatments
Ongoing skin issues can reach beyond the surface, disrupting countless aspects of your daily life. When dealing with persistent redness, itching and inflammation, it's normal to wonder: Is this eczema or psoriasis? These two chronic skin conditions are more common than you may think, affecting millions worldwide. Understanding their differences is key to finding the right path to relief.
In this article, we'll explore the key differences between eczema and psoriasis. You'll learn about their causes and symptoms and how they affect different areas of the body. We'll also discuss diagnosis methods and a range of treatment options that can help manage these conditions.
What are eczema and psoriasis?
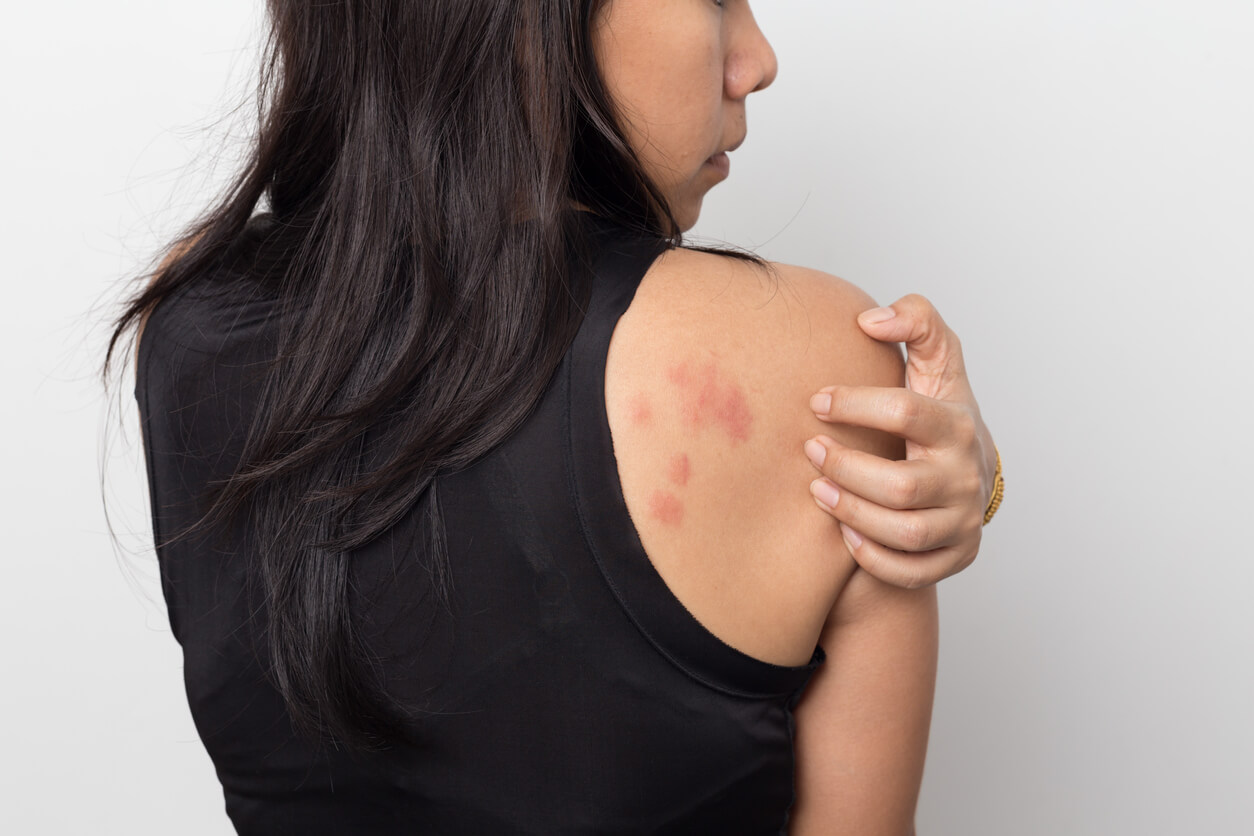
Eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions that cause inflammation, itchiness and irritation. While they might seem similar at first glance, these persistent conditions have their own unique set of symptoms, root causes and triggers.
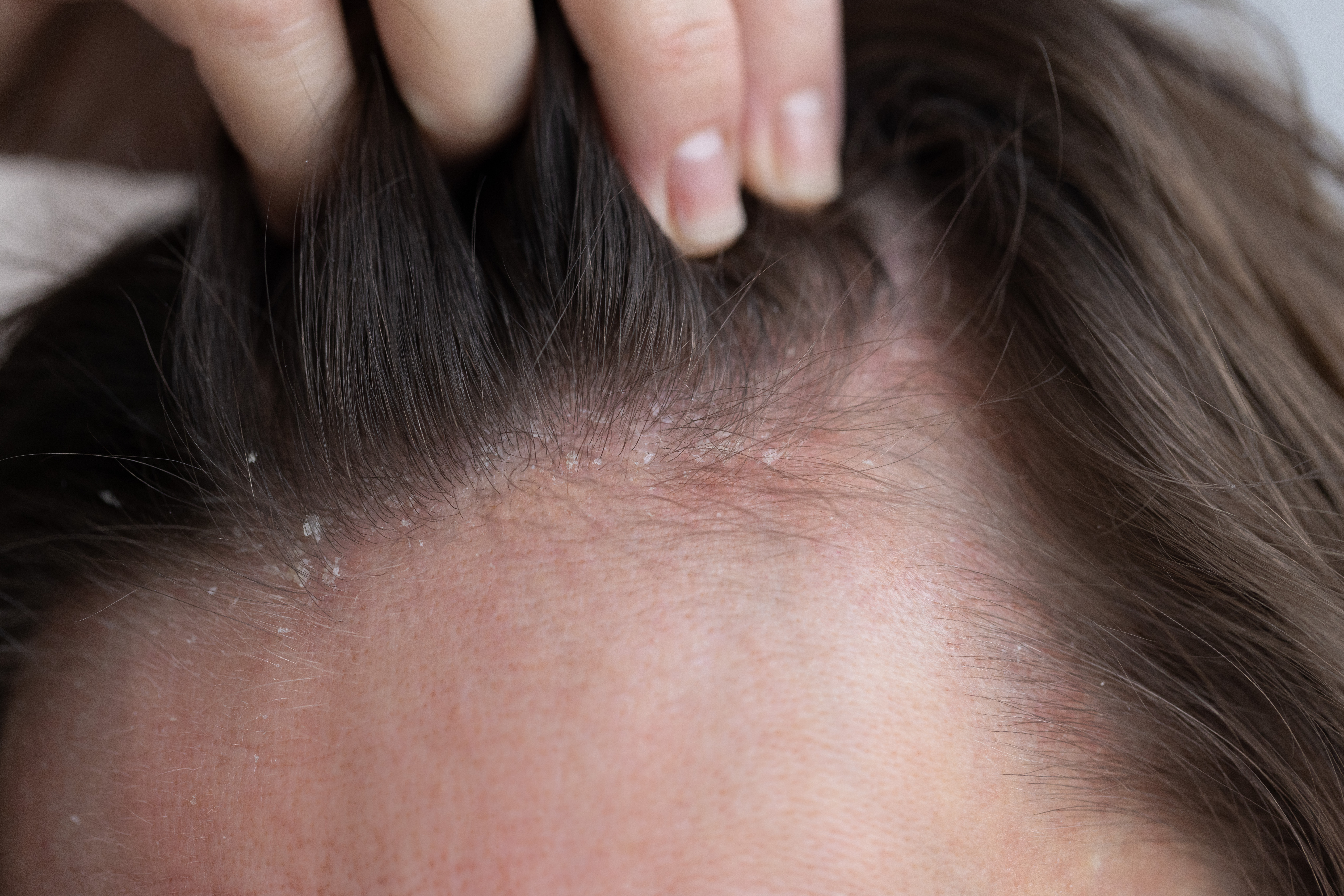
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes patches of skin to become inflamed, itchy and irritated. It's known for coming and going in waves, with periods of flare-ups followed by times of calmer skin. The most common type of eczema is atopic dermatitis (atopic eczema).
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes thick, salmon-pink or red, itchy and flaky patches to appear on the body. These spots can show up anywhere on the body and may appear and disappear over time. It is considered an autoimmune disease. There are several types of psoriasis, the most common being plaque psoriasis.
Symptoms and appearance
While eczema and psoriasis can both cause skin discomfort, their symptoms and appearance differ in several key ways. Understanding these differences can help you better identify which condition you may be dealing with and seek appropriate treatment.
Common eczema symptoms can include:
- Dry, sensitive skin
- Intensely itchy, red, scaly and inflamed patches of skin
- Small raised bumps that may leak clear fluid or form crusts
- Rashes that appear on the inside of elbows, back of knees, neck, wrists and ankles
- Light-colored patches on the skin, often seen in children
Common psoriasis symptoms can include:
- Thick, raised, red patches of dry skin covered with white or silvery scales
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Itching, burning or soreness in affected areas
- Nail changes, such as ridges or discoloration
- Swollen and stiff joints
- Patches that appear on the scalp, back of the knees, elbows, and lower back
Eczema often begins in childhood, with over 85% of cases starting before age 5. Psoriasis symptoms typically begin between ages 20-30 or 50-60. However, both conditions can appear at any age. It's important to note that symptoms can vary from person to person and may change over time.
Is it eczema or psoriasis?
While eczema and psoriasis may share similar symptoms like skin irritation, itching, and redness, it is possible to tell them apart by observing some key differences. Even though the rashes can look similar at first glance, several traits are unique to each condition.
Both eczema and psoriasis can be triggered by extreme temperatures (hot or cold), but eczema flare-ups cause intense itching, while psoriasis causes less intense itchiness but more of a burning sensation.
It is possible to have both eczema and psoriasis at the same time. However, only about 2% of people have both conditions.
Although these clues can help, a dermatologist or primary care provider is best equipped to provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. If you're unsure which condition you're experiencing, it's important to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and care.
Causes and risk factors
The exact root causes of both eczema and psoriasis are not entirely understood. However, a combination of genetic and environmental factors likely play a role in their development. In psoriasis, inherited genes affect the immune system, causing it to mistakenly speed up skin cell growth. This means your skin makes new cells much faster than normal, causing them to pile up on the surface. This leads to its distinctive thick, red, scaly patches.
People with eczema often have a weakened skin barrier, which can be influenced by genetics. This results in skin that is more easily irritated and prone to dryness, allergens and inflammation.
When it comes to risk factors, having a family history of these conditions increases your chances of developing them. For psoriasis, obesity and certain lifestyle factors like smoking play a role. Risk factors for eczema include a family history of allergies, asthma or eczema.
Common triggers
Eczema and psoriasis share some common triggers, like stress and skin injuries. Exposure to triggers can cause flare-ups or worsen symptoms. However, there are also triggers specific to each condition.
Eczema flare-ups can be triggered by:
- Allergens like dust mites, pollen or certain foods
- Hot and humid weather or sudden temperature changes
- Harsh or fragrant soaps and detergents
- Certain fabrics like wool, polyester, nylon, rayon and acrylic
Psoriasis flare-ups can be triggered by:
- Bacterial infections, particularly strep throat
- Cold, dry weather
- Certain medications, including lithium, beta-blockers and certain antimalarial drugs
- Smoking
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Hormonal changes, like puberty and menopause
Treatment options
Eczema and psoriasis can be frustrating and exhausting to manage. Constant itching, uncomfortable flare-ups and visible patches can make even simple daily activities challenging. However, treatment options have come a long way, opening up new possibilities for relief.
Both eczema and psoriasis can benefit from several similar treatment approaches:
- Topical corticosteroid creams, such as betamethasone valerate (Betamethacot)
- Fragrance-free, gentle moisturizers (emollients) and lotions
- Ultraviolet light therapy (phototherapy)
- Oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone (Deltasone)
Specific eczema treatment options can also include:
- Antihistamines, such as cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- Certain immunosuppressive medications, such as azathioprine (Azasan)
Specific psoriasis treatment options can also include:
- Topical creams or ointments containing salicylic acid
- Coal tar 2% foam
- Photochemotherapy (PUVA)
- Certain biologic drugs, such as brodalumab (Siliq)
Remember, treatment effectiveness can vary significantly from person to person. What works well for one person may not be the best fit for another. Always consult your doctor or dermatologist before starting any new medication, even if it's available over the counter.
How Sesame can help
If you're unsure whether you're dealing with eczema or psoriasis, providers on Sesame can help. Book an online dermatology consult today to speak to a top-rated provider who can assess your symptoms, give you a diagnosis and help you establish a treatment plan.
Whether you need help distinguishing between these conditions or require prescription medications, Sesame's network of experienced providers can offer personalized care plans tailored to your specific skin concerns.